Schizophrenia is a psychiatric condition characterized by a wide range of symptoms divided into positive and negative categories. Its origins are believed to stem from the release of excessive dopamine. Therefore, in theory, by decreasing cortical excitability and possibly inhibiting dopamine release, symptoms of positive schizophrenia could be reduced or eliminated. Conversely, increasing cortical excitation and inducing dopamine release could improve negative symptoms.
Positive symptoms involve hyperactivity in the left temporoparietal cortex. Auditory hallucinations may be due to atypical activation of language perception areas. Symptoms include:
- Disorganized speech
- Hallucinations
- Delusions
- Catatonic behavior
Negative symptoms are associated with hypoactivity of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of the brain:
Affective flattening
- Alogia
- Anhedonia
- Avolition
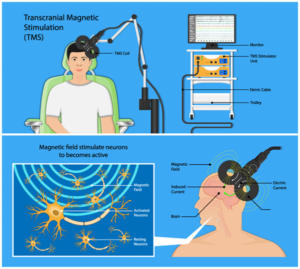
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a neurostimulation technique that uses alternating magnetic fields to induce an electrical current in the brain’s cortex. Neurons depolarize and generate action potentials as a result.
The frequency and severity of auditory hallucinations associated with positive symptoms of schizophrenia may be decreased by targeting low-frequency TMS stimuli to the left temporoparietal cortex.
TMS to the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex can reduce negative cognitive symptoms like working memory, attention, processing speed, and visual/verbal learning with reasoning deficits in reasoning, planning, abstract thinking, and problem-solving.