Redox Biology
Redox biology refers to the study of the balance between oxidation and reduction (redox) reactions in biological systems. These reactions involve the transfer of electrons and are fundamental to the functioning of cells and organisms. Redox reactions are essential for energy production, the maintenance of cellular homeostasis, and various biochemical processes. Understanding redox biology is relevant to mental health because it can have significant implications for the brain’s function and the development of mental disorders. Here’s how redox biology relates to mental health:
-
Energy Production: The brain is a highly energy-demanding organ, and redox reactions are crucial for generating the energy needed for its functions. Mitochondria, the cell’s powerhouses, are central to redox reactions, as they produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of cells. Any disruptions in mitochondrial function and redox balance can impact energy production in the brain, potentially leading to mental health issues.
-
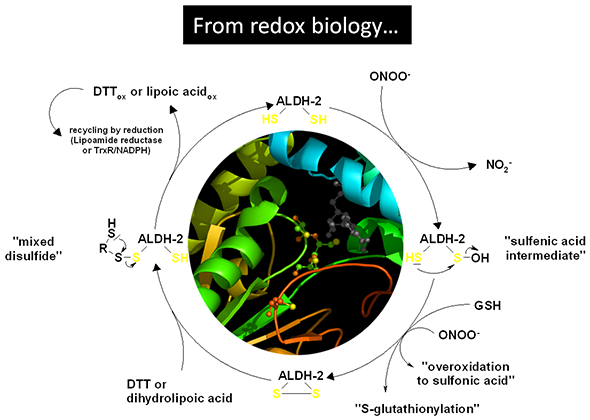
Oxidative Stress: While redox reactions are essential for normal cellular function, an imbalance in the redox state can lead to oxidative stress. Oxidative stress occurs when there is an excess of reactive oxygen species (ROS) compared to antioxidants in the body. Excessive oxidative stress can damage cellular components, including lipids, proteins, and DNA, which can contribute to neurodegenerative disorders and mental health conditions like depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia.
-
Neurotransmitter Regulation: Redox reactions play a role in the synthesis, release, and regulation of neurotransmitters in the brain. Neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, dopamine, and glutamate, are vital for mood regulation, cognition, and emotional well-being. Disruptions in redox balance can affect neurotransmitter levels and functioning, potentially contributing to mood disorders like depression and bipolar disorder.
-
Inflammation: Redox biology is intertwined with the body’s inflammatory response. Chronic inflammation is associated with various mental health conditions, including depression and anxiety. Oxidative stress and inflammation can create a vicious cycle, where each process exacerbates the other, further impacting mental well-being.
Antioxidant Defense: The body has an antioxidant defense system that includes enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase. These enzymes help neutralize ROS and maintain redox balance. Dysregulation of this defense system can increase vulnerability to mental health disorders.
Neuroprotection: Maintaining redox balance is critical for protecting neurons from damage and promoting their survival. Disruptions in redox biology can make neurons more susceptible to injury, which may contribute to neurodegenerative disorders and cognitive impairment.